Sometimes it may be useful to convert a Jupyter notebook into a Python executable script. Once your notebook is opened in OOD you can select File > Export Notebook As … > Export Notebook to Executable Script:
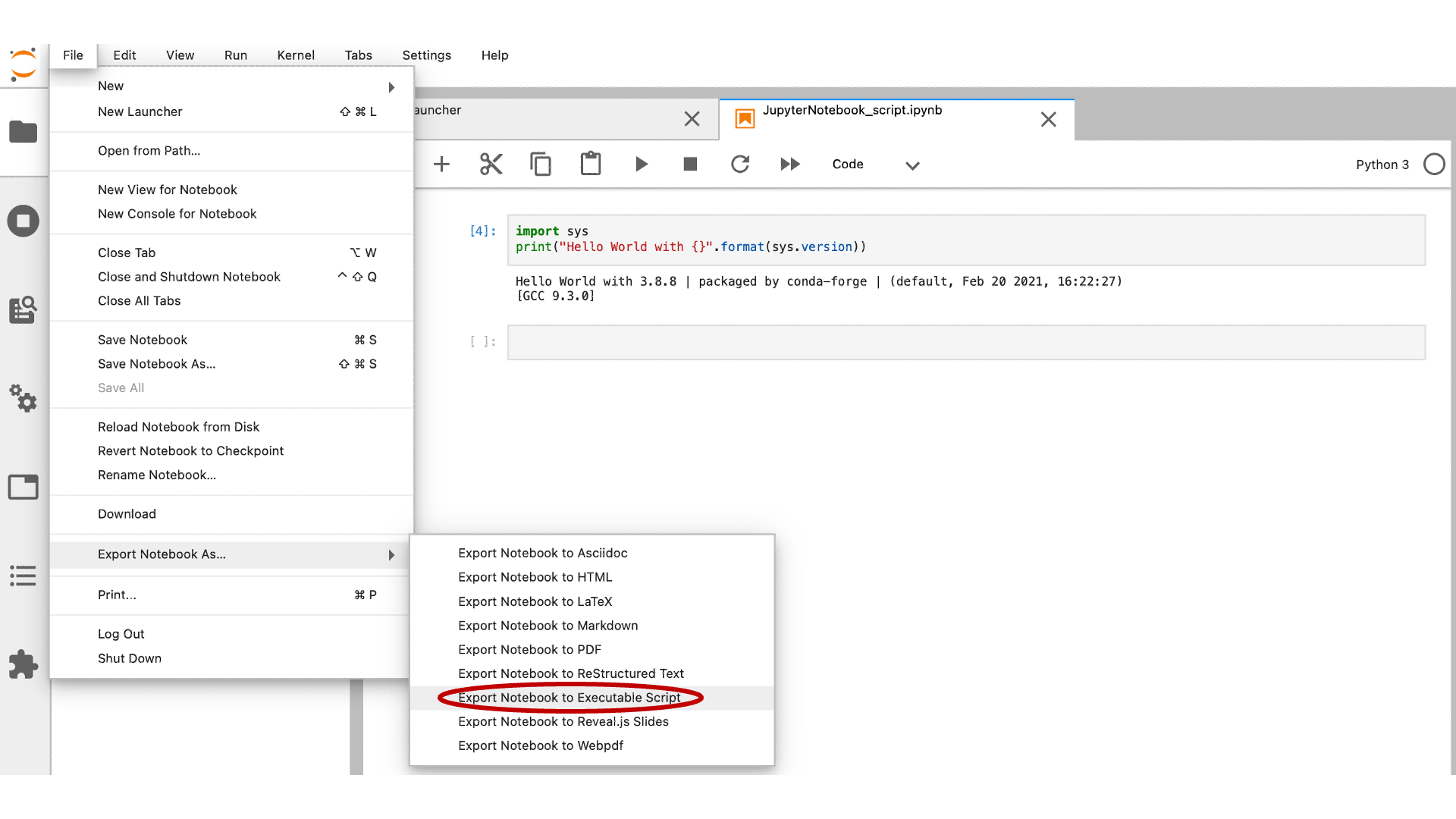
This will download a Python executable with a ‘.py’ extension into your local computer’s Downloads folder. Your notebook may also show “Download as” instead of “Export Notebook As …”. Either of these selections will allow you to download a Python executable.
This script can be copied to the HPC system in the working directory where JupyterLab was accessing the notebook. Information on transferring files to and from Rivanna can be found here.
Notebooks can also be converted directly on the command line. This can be done by loading jupyterlab and running jupyter nbconvert --to script /path/to/ipynb, where /path/to/ipynb is the location of the notebook file:
module load jupyterlab
jupyter nbconvert --to script /path/to/ipynb
A Slurm submission script is required to execute the Python executable. JupyterLab on OOD provides a web form that requests resources for your job to run on a compute node. Let’s look at the web form from OOD:
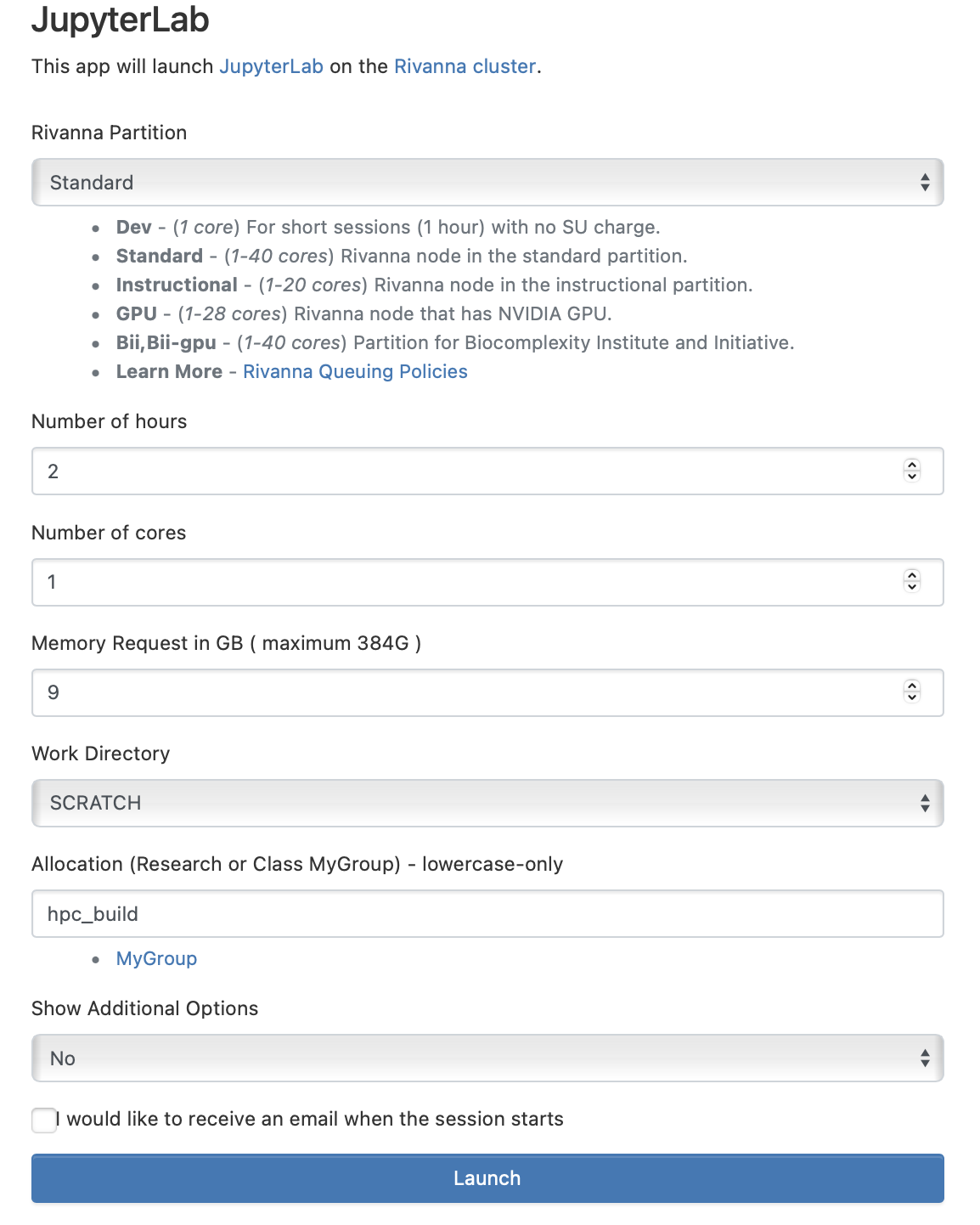
We see that the form requests a partition, the time in hours, the number of cores, the requested memory, the working directory, and your UVA HPC allocation. Once you click “Launch”, your job is submitted and requests these specifications on a compute node. The same can be done by writing a Slurm submission script. The script below mirrors the specifications set in the web form. We’ll call this script submit_jup.slurm.
#!/bin/bash
#SBATCH -p standard
#SBATCH -t 02:00:00
#SBATCH -c 1
#SBATCH --mem=9GB
#SBATCH -A hpc_build
module purge
module load miniforge
python JupyterNotebook_script.py
Now that everything is ready, all that needs to be done is to submit submit_jup.slurm. This is accomplished by typing sbatch submit_jup.slurm on the command line in the same directory of the Slurm script and Python script. Your job will launch on a compute node and write its output to a Slurm output file. Since this script only prints standard output the Slurm output file will contain the same information as the notebook.
Hello World with 3.8.8 | packaged by conda-forge | (default, Feb 20 2021, 16:22:27)
[GCC 9.3.0]
More information on using Slurm on the HPC system can be found here.
If your code requires a specific conda environment, you can specify source activate <environment name> below the module commands in the Slurm script to activate the environment:
#!/bin/bash
#SBATCH -p standard
#SBATCH -t 02:00:00
#SBATCH -c 1
#SBATCH --mem=9GB
#SBATCH -A hpc_build
module purge
module load miniforge
source activate <environment name>
python JupyterNotebook_script.py